三、Pre-rendering
大约 18 分钟约 5541 字
(一)Pre-rendering —— 预渲染
1. What?
- 默认情况下,
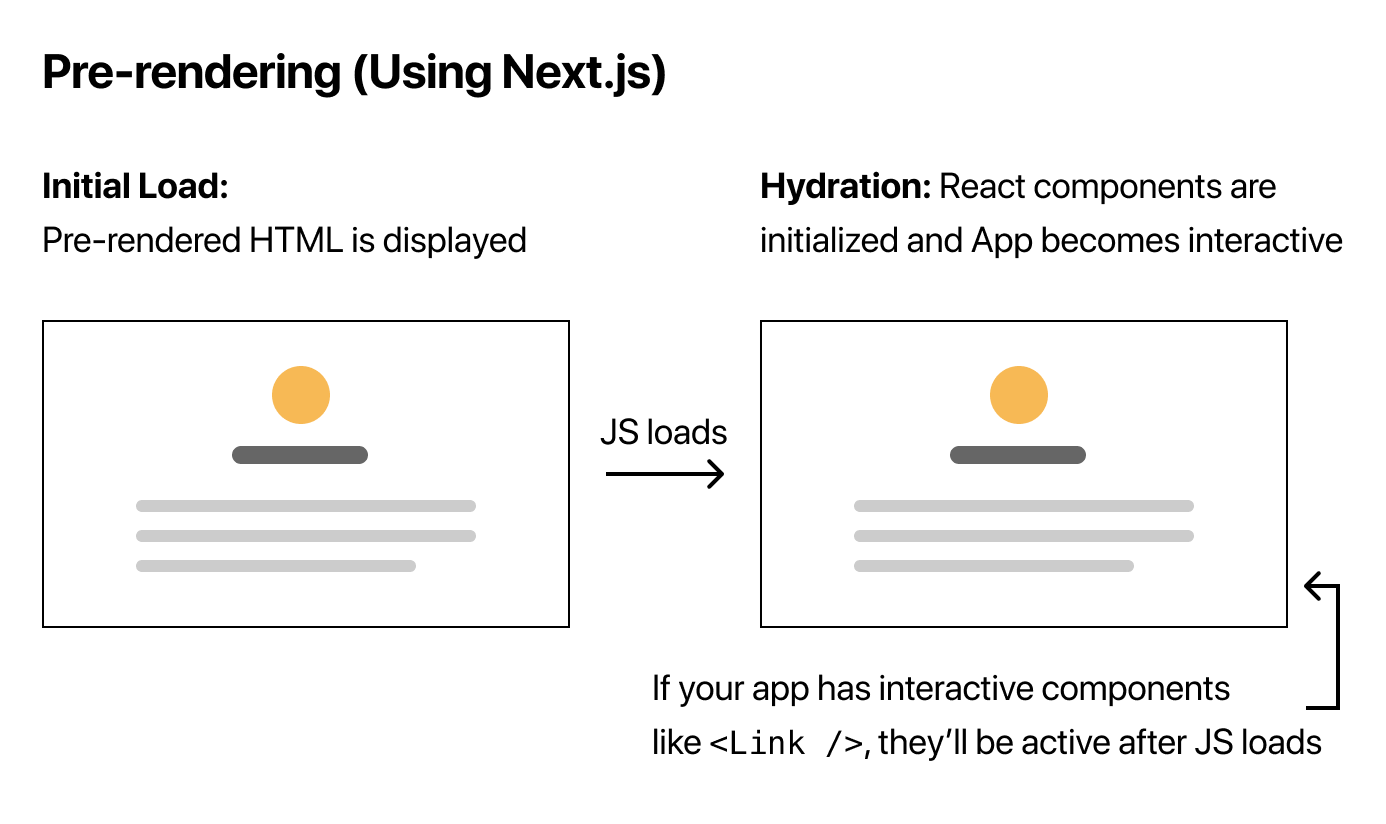
NextJS预渲染应用程序中的每个页面 - 预渲染指提前为每个页面生成
HTML,而不是全部由客户端JavaScript完成 NextJS应用审查时可以看到页面组成的各种元素- 预渲染指的是在应用程序中生成带有页面所需数据的
HTML的过程 NextJS支持两种形式的预渲染Static Generation:静态渲染Server-side Rendering:服务器渲染
2. Why?
- 预渲染提高性能
- 在
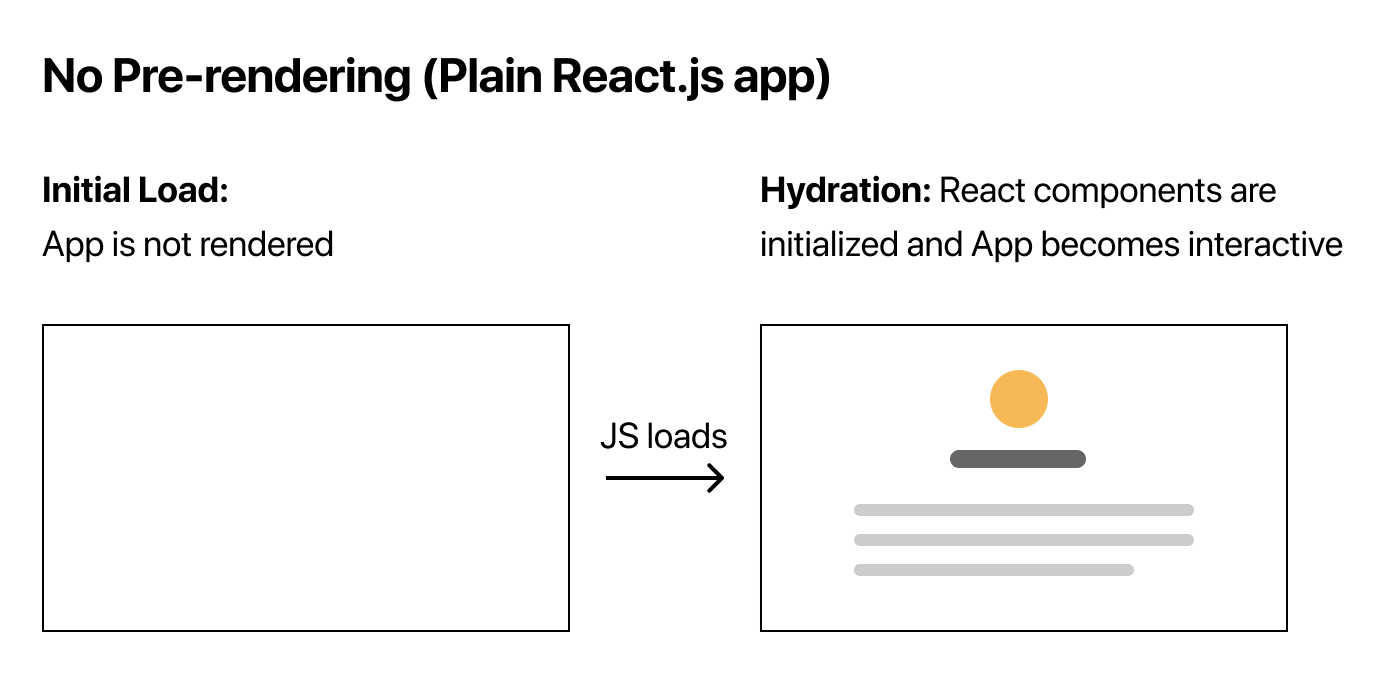
React应用中,需要等待JavaScript被执行 - 可能需要从外部 API 获取数据后,再渲染 UI
- 用户需要等待一段时间
- 使用预渲染页面,用户可以先看到渲染后的
HTML,加载速度更快
- 在
- 预渲染有助于
SEO- 建立一个博客或电子商务网站,需要考虑
SEO - 在
React应用中,搜索引擎只能看到<div id="root"></div> - 当搜索引擎搜索到预渲染页面时,所有的页面元素都出现在页面中,有助于索引该页面
- 建立一个博客或电子商务网站,需要考虑
3. Two forms
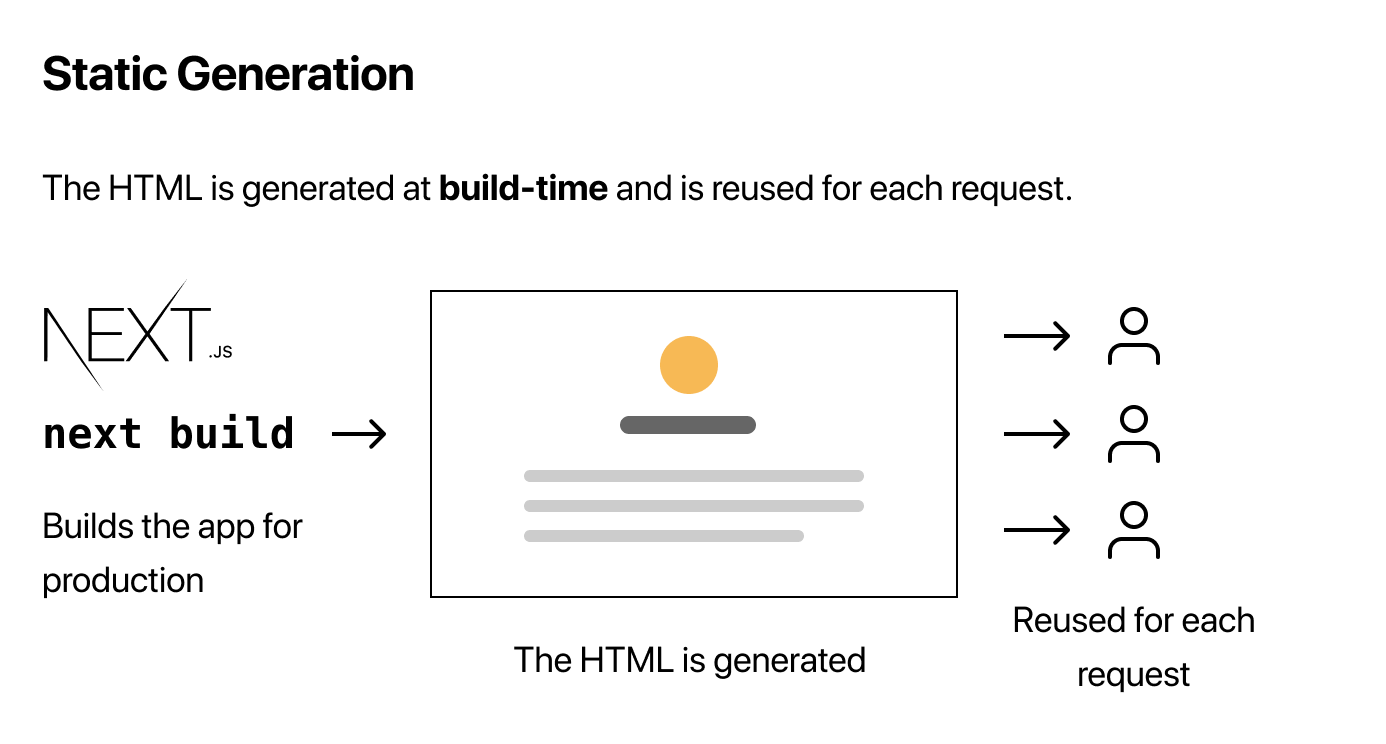
- Static Generation (SG)
HTML是在构建时静态渲染的,然后对构建的页面进行缓存并为每个请求重用- 对于
getStaticPaths和fallback: true的动态页面,页面是在初始请求时渲染的,不是在构建时渲染的
- Server-side Rendering (SSR)
(二)Static Generation —— SG 静态渲染
- 默认在没有任何配置的情况下,当我们为生产环境构建应用程序时,会静态生成应用程序中的每个页面
- 这允许页面被
CDN缓存,并被搜索引擎索引
1. What?
- 在构建时生成
HTML页面的预渲染方法 - 构成网页内容的所有数据是在构建应用程序时预先生成的
- 尽可能使用
SG方法预渲染页面 - 页面可以只构建一次,由
CDN缓存,几乎立即返回给客户端 - 适用于:博客页面、电子商务产品页面、文档和市场营销页面等
2. How?
- 默认情况下,
NextJS将预渲染应用程序中的每个页面 - Prod Server 生产环境
- 优化的构建只创建一次,然后部署该构建
- 一旦构建完成,就不需要随时更改代码
- Dev Server 开发环境
- 能够对代码进行更改,且希望这些代码能够立即反映在浏览器中
- 对于生产构建,当我们运行构建命令时,页面将被预渲染一次
- 对于开发模式,页面会为每次发出的页面请求进行预呈现
3. Static Generation with getStaticProps
getStaticProps只在服务器端运行- 永远不会在客户端运行
- 该函数内部编写的代码甚至不会包含在发送到浏览器的
JS包中
- 可以直接在
getStaticProps中编写服务器端的代码- 例如使用
fs模块访问文件系统或查询数据库等相关代码 - 无需担心代码中包含
API键,因为这些代码不会进入浏览器
- 例如使用
getStaticProps只允许在页面中运行(pages/**),不能从常规组件文件中运行(components/**)- 仅用于预渲染,不能用于客户端数据获取
getStaticProps应该返回一个对象,该对象应该包含一个props键,该键也应该是一个对象getStaticProps会在构建时运行- 在开发环境下,会在每个请求时运行
1)pages/index.js
import Link from "next/link";
function Home() {
return (
<>
<h1>Next JS pre-rendering</h1>
<Link href="/users">
<a>Users</a>
</Link>
</>
);
}
export default Home;
2)pages/users.js
import User from "../components/user";
function UserList({ users }) {
return (
<>
<h1>List of users</h1>
{users.map((user) => {
return (
<div key={user.id}>
<User user={user} />
</div>
);
})}
</>
);
}
export default UserList;
export async function getStaticProps() {
const response = await fetch("https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/users");
const data = await response.json();
console.log(data); // view in the terminal
return {
props: {
users: data,
},
};
}
3)components/user.js
function User({ user }) {
return (
<>
<p>{user.name}</p>
<p>{user.email}</p>
</>
);
}
export default User;
4.Link Pre-fetching
- 默认情况下,使用静态生成的页面,其视口中的任何
<Link />组件(初始化或通过滚动)都将被预取(包括相应的数据) - 当一个定义了
getStaticProps的页面在构建时预渲染时,除了页面本身的HTML文件外,NextJS还生成了一个JSON文件,包含了getStaticProps的运行结果 JSON文件将用于客户端通过next/link或next/router进行路由跳转时渲染- 当导航到一个使用
getStaticProps预渲染的页面时,NextJS将获取JSON文件(在构建时预计算),并将其用作创建客户端页面组件的props属性值 - 客户端页面转换器不会调用
getStaticProps,因为它只使用导出的JSON文件
5.总结
Static Generation静态渲染是一种在构建时生成HTML页面的预渲染方法- 使用
getStaticProps函数导出外部数据 - 构建时会生成
HTML、JavaScript和JSON文件 - 如果从一个路由直接跳转到另一个页面路由,客户端将使用从服务器预取的
JavaScript和JSON文件创建页面
6. SSG(Static Side Generation) with Dynamic Parameters
- 动态路由页面中的
getStaticProps可能接收到不同类型不同大小的动态参数,无法正确实现页面预渲染
1)pages/index.js
import Link from "next/link";
function Home() {
return (
<>
<h1>Next JS pre-rendering</h1>
<Link href="/users">
<a>Users</a>
</Link>
<hr />
<Link href="/posts">
<a>Posts</a>
</Link>
</>
);
}
export default Home;
2)pages/posts/index.js
import Link from "next/link";
function PostList({ posts }) {
return (
<>
<h1>List of Posts</h1>
{posts.map((post) => {
return (
<div key={post.id}>
<Link href={`posts/${post.id}`} passHref>
<h2>
{post.id} {post.title}
</h2>
</Link>
<hr />
</div>
);
})}
</>
);
}
export default PostList;
export async function getStaticProps() {
const response = await fetch("https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts");
const data = await response.json();
return {
props: {
posts: data.slice(0, 3),
},
};
}
3)pages/posts/[postId].js
function Post({ post }) {
return (
<>
<h2>
{post.id} {post.title}
</h2>
<p>{post.body}</p>
</>
);
}
export default Post;
export async function getStaticProps(context) {
const { params } = context;
const response = await fetch(`https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts/${params.postId}`);
const data = await response.json();
return {
props: {
post: data,
},
};
}
7. SSG with getStaticPaths
- 使用
getStaticPaths在预渲染时声明动态路由将会接收到的可能值
1)pages/posts/[postId].js
function Post({ post }) {
return (
<>
<h2>
{post.id} {post.title}
</h2>
<p>{post.body}</p>
</>
);
}
export default Post;
export async function getStaticPaths() {
return {
paths: [
{
params: {
postId: "1",
},
},
{
params: {
postId: "2",
},
},
{
params: {
postId: "3",
},
},
],
fallback: false,
};
}
export async function getStaticProps(context) {
const { params } = context;
const response = await fetch(`https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts/${params.postId}`);
const data = await response.json();
return {
props: {
post: data,
},
};
}
8. Fetching Paths for getStaticPaths
1)pages/posts/[postId].js
function Post({ post }) {
return (
<>
<h2>
{post.id} {post.title}
</h2>
<p>{post.body}</p>
</>
);
}
export default Post;
export async function getStaticPaths() {
const response = await fetch("https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts");
const data = await response.json();
const paths = data.map((post) => {
return {
params: {
postId: `${post.id}`,
},
};
});
return {
paths,
fallback: false,
};
}
export async function getStaticProps(context) {
const { params } = context;
const response = await fetch(`https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts/${params.postId}`);
const data = await response.json();
return {
props: {
post: data,
},
};
}
2)pages/posts/index.js
import Link from "next/link";
function PostList({ posts }) {
return (
<>
<h1>List of Posts</h1>
{posts.map((post) => {
return (
<div key={post.id}>
<Link href={`posts/${post.id}`} passHref>
<h2>
{post.id} {post.title}
</h2>
</Link>
<hr />
</div>
);
})}
</>
);
}
export default PostList;
export async function getStaticProps() {
const response = await fetch("https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts");
const data = await response.json();
return {
props: {
posts: data,
},
};
}
9. getStaticPaths fallback false
- 从
getStaticPaths返回的路径将在构建时被渲染为HTML文件 - 当
fallback设为false时,任何没有从getStaticPaths中返回的路径都会跳转到 404 页面 - When?
- 如果需要预渲染的路径较少,或者不经常添加新页面,则
false值最合适 - 如只有几篇文章的博客网站
- 如果需要预渲染的路径较少,或者不经常添加新页面,则
1)pages/posts/index.js
import Link from "next/link";
function PostList({ posts }) {
return (
<>
<h1>List of Posts</h1>
{posts.map((post) => {
return (
<div key={post.id}>
<Link href={`posts/${post.id}`} passHref>
<h2>
{post.id} {post.title}
</h2>
</Link>
<hr />
</div>
);
})}
</>
);
}
export default PostList;
export async function getStaticProps() {
const response = await fetch("https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts");
const data = await response.json();
return {
props: {
posts: data.slice(0, 3),
},
};
}
2)pages/posts/[postId].js
function Post({ post }) {
return (
<>
<h2>
{post.id} {post.title}
</h2>
<p>{post.body}</p>
</>
);
}
export default Post;
export async function getStaticPaths() {
return {
paths: [
{
params: {
postId: "1",
},
},
{
params: {
postId: "2",
},
},
{
params: {
postId: "3",
},
},
],
fallback: false,
};
}
export async function getStaticProps(context) {
const { params } = context;
const response = await fetch(`https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts/${params.postId}`);
const data = await response.json();
return {
props: {
post: data,
},
};
}
10. getStaticPaths fallback true
- 从
getStaticPaths返回的路径将在构建时通过getStaticProps被渲染为HTML文件 - 当
fallback设为true时,任何没有从getStaticPaths中返回的路径不会跳转到 404 页面,NextJS将在对该路径的第一次请求时提供页面的“备用”版本 NextJS会在后台静态生成请求路径对应的HTML和JSON文件,包括运行其中的getStaticProps- 运行完成后,浏览器会接收到当前请求路径对应的
JSON文件,用于自动渲染当前页面需要的props属性。从用户角度看,页面会从“备用”版本切换到完整版本 - 与此同时,
NextJS会保持跟踪预渲染页面的新列表,对同一路径的后续请求返回相同的渲染结果,就像在构建时预渲染其他页面一样 - When?
- 当有大量依赖于数据的静态页面时,
fallback设为true最合适 - 如大型的电子商务网站
- 当希望预先渲染所有产品页面,但是几千个产品构建需要很长时间,此时可以静态生成一小部分受欢迎的产品,并使用
fallback: true渲染剩余产品 - 当请求一个尚未渲染完成的页面时,用户会看到带有加载指示器的页面
- 不久之后,当
getStaticProps执行完成时页面将呈现正常的数据,从那时起每个相同页面的请求都将获得静态预渲染的页面 - 这确保了用户总是有一个快速的体验,同时保证快速构建和静态渲染的好处
- 当有大量依赖于数据的静态页面时,
1)pages/posts/index.js
import Link from "next/link";
function PostList({ posts }) {
return (
<>
<h1>List of Posts</h1>
{posts.map((post) => {
return (
<div key={post.id}>
<Link href={`posts/${post.id}`} passHref>
<h2>
{post.id} {post.title}
</h2>
</Link>
<hr />
</div>
);
})}
</>
);
}
export default PostList;
export async function getStaticProps() {
const response = await fetch("https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts");
const data = await response.json();
return {
props: {
// posts: data.slice(0, 3),
posts: data,
},
};
}
2)pages/posts/[postId].js
import { useRouter } from "next/router";
function Post({ post }) {
// 访问未从getStaticPaths中返回的路径时,不会跳转404,而是预渲染下面返回的,等后台页面加载完成后再显示完整的页面
const router = useRouter();
if (router.isFallback) {
return <h1>Loading...</h1>;
}
return (
<>
<h2>
{post.id} {post.title}
</h2>
<p>{post.body}</p>
</>
);
}
export default Post;
export async function getStaticPaths() {
return {
paths: [
{
params: {
postId: "1",
},
},
{
params: {
postId: "2",
},
},
{
params: {
postId: "3",
},
},
],
fallback: true,
};
}
export async function getStaticProps(context) {
const { params } = context;
const response = await fetch(`https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts/${params.postId}`);
const data = await response.json();
// 访问超出API数据范围的id,如101,此时会返回404页面
if (!data.id) {
return {
notFound: true,
};
}
console.log(`Generating page for /posts/${params.postId}`);
return {
props: {
post: data,
},
};
}
11. getStaticPaths fallback blocking
- 从
getStaticPaths返回的路径将在构建时通过getStaticProps被渲染为HTML文件 - 当
fallback设为blocking时,任何没有从getStaticPaths中返回的路径不会跳转到 404 页面,相反NextJS将在对该路径的第一次请求时在服务器上渲染页面并返回生成的HTML - 完成后,浏览器会接收到当前请求路径对应的
HTML文件。从用户角度看,页面会从“浏览器正在请求页面”过渡到“加载整个页面”,没有加载/回退状态的闪动 - 与此同时,
NextJS会保持跟踪预渲染页面的新列表,对同一路径的后续请求返回相同的渲染结果,就像在构建时预渲染其他页面一样 - When?
- 在用户体验层面上,如果等待时间只有几微秒,有时人们更希望页面加载时没有加载指示器,而是展示部分页面,这有助于避免布局转移
- 一些爬虫程序不支持
JavaScript,先渲染加载页面后加载完整页面就会导致某些问题
1)pages/posts/index.js
import Link from "next/link";
function PostList({ posts }) {
return (
<>
<h1>List of Posts</h1>
{posts.map((post) => {
return (
<div key={post.id}>
<Link href={`posts/${post.id}`} passHref>
<h2>
{post.id} {post.title}
</h2>
</Link>
<hr />
</div>
);
})}
</>
);
}
export default PostList;
export async function getStaticProps() {
const response = await fetch("https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts");
const data = await response.json();
return {
props: {
// posts: data.slice(0, 3),
posts: data,
},
};
}
2)pages/posts/[postId].js
function Post({ post }) {
return (
<>
<h2>
{post.id} {post.title}
</h2>
<p>{post.body}</p>
</>
);
}
export default Post;
export async function getStaticPaths() {
return {
paths: [
{
params: {
postId: "1",
},
},
{
params: {
postId: "2",
},
},
{
params: {
postId: "3",
},
},
],
fallback: "blocking",
};
}
export async function getStaticProps(context) {
const { params } = context;
const response = await fetch(`https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts/${params.postId}`);
const data = await response.json();
// 访问超出API数据范围的id,如101,此时会返回404页面
if (!data.id) {
return {
notFound: true,
};
}
console.log(`Generating page for /posts/${params.postId}`);
return {
props: {
post: data,
},
};
}
12.SG 总结 & 问题
1)Static Generation
Static Generation静态渲染是一种在构建时生成HTML页面的预渲染方法- 预渲染的静态页面可以推送到
CDN、缓存并几乎立即提供给全球各地的客户端 - 静态内容对于
SEO来说更快更好,因为它们会立即被搜索引擎索引到 - 使用
getStaticProps进行数据获取的静态渲染和使用getStaticPaths进行动态路由的静态渲染,似乎适用于生产中的各种应用
2)Issue
- 构建时间与应用程序中的页面数量成正比
- 页面一旦生成,到重新构建应用前都可能包含过期数据
(三)Incremental Static Regeneration —— ISR 增量静态再生
- 只需要更新部分需要更改的页面,不必重新构建整个应用程序
- 通过
ISR,NextJS允许在构建应用程序后更新静态页面,可以静态地生成单个页面,不需要重新构建整个站点,有效地解决了处理陈旧数据的问题 - How?
- 在
getStaticProps函数中,除了props键外还可以指定revalidate键,值是重新生成页面的秒数
- 在
1.引出 ISR
- 项目构建后,修改
db.json返回的数据,页面并没有展示最新的数据 - 首次访问未从
getStaticPaths中返回的路径的页面时,展示的是最新的数据,一经访问后再次修改数据,则页面数据不更新
yarn add json-server
yarn serve-json
yarn build
yarn start
1)db.json
{
"products": [
{
"id": 1,
"title": "Product 1",
"price": 1000,
"description": "Description 1"
},
{
"id": 2,
"title": "Product 2",
"price": 2000,
"description": "Description 2"
},
{
"id": 3,
"title": "Product 3",
"price": 2500,
"description": "Description 3"
}
]
}
2)package.json
{
"scripts": {
"serve-json": "json-server --watch db.json --port 4000"
}
}
3)pages/products/index.js
function ProductList({ products }) {
return (
<>
<h1>List of products</h1>
{products.map((product) => {
return (
<div key={product.id}>
<h2>
{product.id} {product.title} {product.price}
</h2>
<hr />
</div>
);
})}
</>
);
}
export default ProductList;
export async function getStaticProps() {
const response = await fetch("http://localhost:4000/products");
const data = await response.json();
return {
props: {
products: data,
},
};
}
4)pages/products/[productId].js
import { useRouter } from "next/router";
function Product({ product }) {
const router = useRouter();
if (router.isFallback) {
return <div>Loading...</div>;
}
return (
<div>
<h2>
{product.id} {product.title} {product.price}
</h2>
<p>{product.description}</p>
<hr />
</div>
);
}
export default Product;
export async function getStaticProps(context) {
const { params } = context;
const response = await fetch(`http://localhost:4000/products/${params.productId}`);
const data = await response.json();
return {
props: {
product: data,
},
};
}
export async function getStaticPaths() {
return {
paths: [
{
params: {
productId: "1",
},
},
],
fallback: true,
};
}
2.revalidate
1)pages/products/index.js
function ProductList({ products }) {
return (
<>
<h1>List of products</h1>
{products.map((product) => {
return (
<div key={product.id}>
<h2>
{product.id} {product.title} {product.price}
</h2>
<hr />
</div>
);
})}
</>
);
}
export default ProductList;
export async function getStaticProps() {
console.log("Generating / Regenerating ProductList");
const response = await fetch("http://localhost:4000/products");
const data = await response.json();
return {
props: {
products: data,
},
// 每隔10s重新验证当前列表数据是否为最新数据
revalidate: 10,
};
}
2)pages/products/[productId].js
import { useRouter } from "next/router";
function Product({ product }) {
const router = useRouter();
if (router.isFallback) {
return <div>Loading...</div>;
}
return (
<div>
<h2>
{product.id} {product.title} {product.price}
</h2>
<p>{product.description}</p>
<hr />
</div>
);
}
export default Product;
export async function getStaticProps(context) {
const { params } = context;
console.log(`Regenerating product ${params.productId}`);
const response = await fetch(`http://localhost:4000/products/${params.productId}`);
const data = await response.json();
return {
props: {
product: data,
},
revalidate: 10,
};
}
export async function getStaticPaths() {
return {
paths: [
{
params: {
productId: "1",
},
},
],
fallback: true,
};
}
3.Re-generation
- 只有当用户在
revalidate配置的时间之后发出请求时,才会触发重新渲染 - 如果用户访问了产品详细信息页面,但一整天都没有其他用户访问该页面,则不会触发重新渲染
revalidate: 10不表示每 10s 自动重新渲染一次页面,它只是表示在此时间之后,如果用户发出请求,则必须触发重新渲染的时间- 重新渲染也可能失败,之前缓存的
HTML可以一直使用,直到后续的重新渲染成功
(四)Server-side Rendering —— SSR 服务端渲染
1. SG 存在的问题
1)无法在请求时获取数据
- 由于不能为每个请求获取数据,页面上会展示过期数据
- 假设正在创建一个新闻网站,内容是非常动态的,因为几乎每秒钟都可以发布新的文章,
getStaticProps将在构建时获取新闻,这并不合适 getStaticPaths可以获取初始请求上的数据,但随后它将被缓存以供后续请求使用ISR静态增量渲染可能有所帮助,但如果revalidate: 1,当后台正在重新渲染时,页面并不会总是看到最新消息
2)无法访问传入的请求
- 当需要获取的数据是特定于用户时,无法获取到需要的数据
- 假设正在创建一个类似于 Twitter 的网站,作为用户应该能看到基于兴趣个性化的推文,这些推文也需要
SEO友好,因为是任何人都可以看到的公共内容 - 为了获取特定于用户的推文,我们需要
userId,只有当项目能够访问传入请求时才能获取这一信息 - 可以在客户端使用
useEffect实现,但这意味着SEO不友好
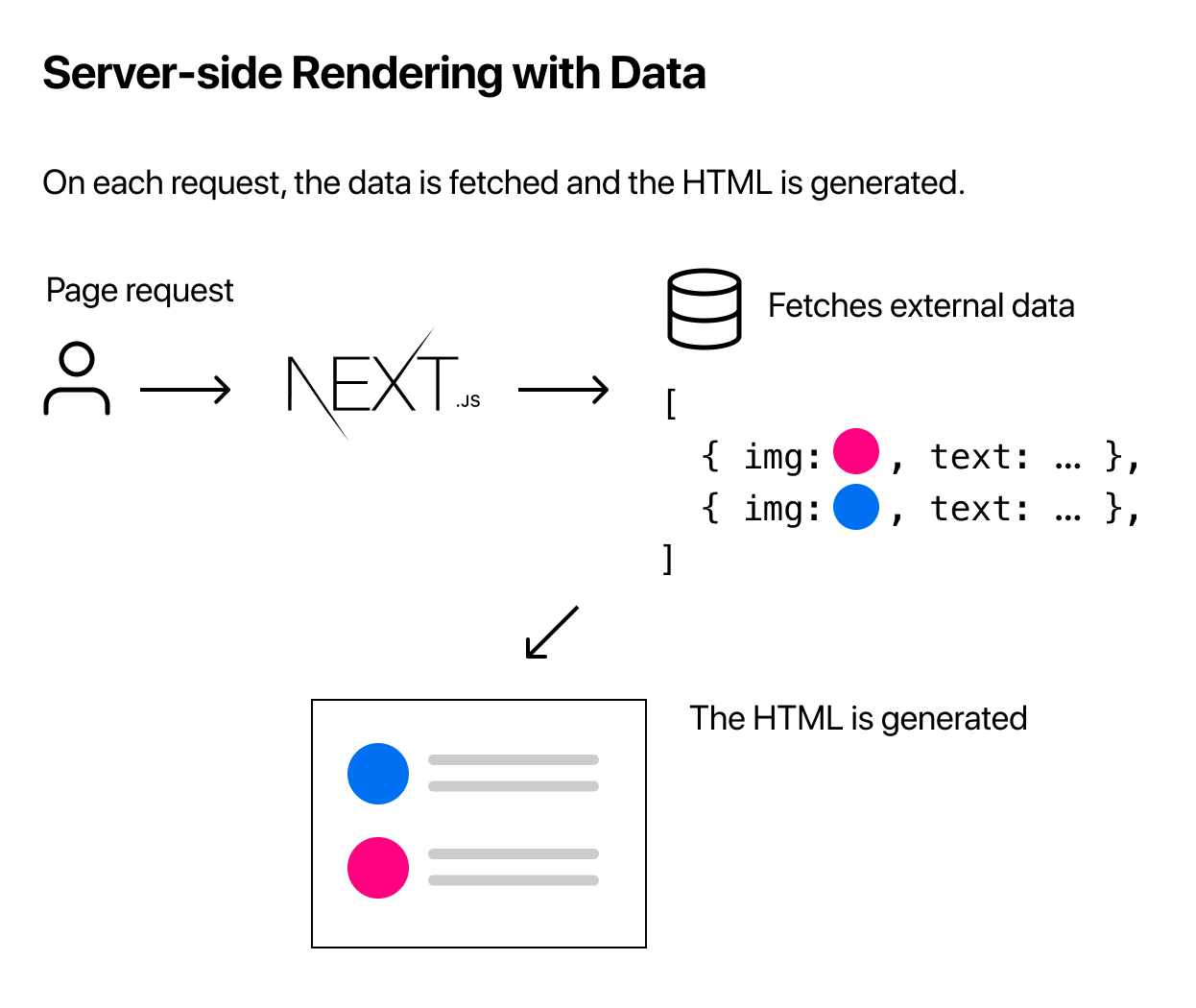
2. What?
NextJS允许在请求时而不是在构建时预渲染页面- 每个传入的请求都会生成
HTML - 当需要获取每个请求的数据时,或者当需要获取个性化数据以优化
SEO时,SSR是必需的
3. SSR with getServerSideProps
getServerSideProps只在服务器端运行- 该函数永远不会在客户端运行
- 函数内的代码不会包含在发送到浏览器的
JS包中
- 可以直接在
getServerSideProps内编写服务器端的代码- 使用
fs模块访问文件系统或查询数据库都可以在函数内完成 - 不必担心函数内包含 API 键,因为代码不会进入浏览器
- 使用
getServerSideProps只允许在路由页面中运行,不能在常规组件中运行- 仅用于预渲染,不能用于客户端数据获取
getServerSideProps应该返回一个对象,该对象包含一个props键,该键也是一个对象getServerSideProps将在请求页面时运行
1)db.json
{
"news": [
{
"id": 1,
"title": "News Article 1",
"description": "Description 1",
"category": "sports"
},
{
"id": 2,
"title": "News Article 2",
"description": "Description 2",
"category": "politics"
},
{
"id": 3,
"title": "News Article 3",
"description": "Description 3",
"category": "sports"
}
],
"products": [
{
"id": 1,
"title": "Product 1",
"price": 1000,
"description": "Description 1"
},
{
"id": 2,
"title": "Product 2",
"price": 2000,
"description": "Description 2"
},
{
"id": 3,
"title": "Product 3",
"price": 2500,
"description": "Description 3"
}
]
}
2)pages/news/index.js
function NewsArticleList({ articles }) {
return (
<>
<h1>List of News Articles</h1>
{articles.map((article) => {
return (
<div key={article.id}>
<h2>
{article.id} {article.title} | {article.category}
</h2>
</div>
);
})}
</>
);
}
export default NewsArticleList;
export async function getServerSideProps() {
const response = await fetch("http://localhost:4000/news");
const data = await response.json();
return {
props: {
articles: data,
},
};
}
4. SSR with Dynamic Parameters
1)pages/news/[category].js
function ArticleListByCategory({ articles, category }) {
return (
<>
<h1>
Showing news for category <i>{category}</i>
</h1>
{articles.map((article) => {
return (
<div key={article.id}>
<h2>
{article.id} {article.title}
</h2>
<p>{article.description}</p>
<hr />
</div>
);
})}
</>
);
}
export default ArticleListByCategory;
export async function getServerSideProps(context) {
const { params } = context;
const { category } = params;
const response = fetch(`http://localhost:4000/news?category=${category}`);
const data = response.json();
return {
props: {
articles: data,
category,
},
};
}
5. getServerSideProps context
1)pages/news/[category].js
function ArticleListByCategory({ articles, category }) {
return (
<>
<h1>
Showing news for category <i>{category}</i>
</h1>
{articles.map((article) => {
return (
<div key={article.id}>
<h2>
{article.id} {article.title}
</h2>
<p>{article.description}</p>
<hr />
</div>
);
})}
</>
);
}
export default ArticleListByCategory;
export async function getServerSideProps(context) {
const { params, req, res, query } = context;
console.log(query);
console.log(req.headers.cookie);
res.setHeader("Set-Cookie", ["name=IKUKO"]);
const { category } = params;
const response = fetch(`http://localhost:4000/news?category=${category}`);
const data = response.json();
return {
props: {
articles: data,
category,
},
};
}
(五)Client-side Data Fetching —— 客户端数据获取
1.两种形式的预渲染
Static Generation静态渲染Server-side Rendering服务器端渲染
2.获取数据
getStaticPropsgetServerSideProps
3.客户端数据获取
- 某些页面不需要预渲染数据,如用户 Dashboard 页面
- 某些用户私有的需登录后才可以访问的页面
- 不需要预渲染数据,可以依赖客户端数据获取
1)db.json
{
"dashboard": {
"posts": 5,
"likes": 100,
"followers": 20,
"following": 50
},
"news": [
{
"id": 1,
"title": "News Article 1",
"description": "Description 1",
"category": "sports"
},
{
"id": 2,
"title": "News Article 2",
"description": "Description 2",
"category": "politics"
},
{
"id": 3,
"title": "News Article 3",
"description": "Description 3",
"category": "sports"
}
],
"products": [
{
"id": 1,
"title": "Product 1",
"price": 1000,
"description": "Description 1"
},
{
"id": 2,
"title": "Product 2",
"price": 2000,
"description": "Description 2"
},
{
"id": 3,
"title": "Product 3",
"price": 2500,
"description": "Description 3"
}
]
}
2)pages/dashboard.js
import { useState, useEffect } from "react";
function Dashboard() {
const [isLoading, setIsLoading] = useState(true);
const [dashboardData, setDashboardData] = useState(null);
useEffect(() => {
async function fetchDashboardData() {
const response = await fetch("http://localhost:4000/dashboard");
const data = await response.json();
setDashboardData(data);
setIsLoading(false);
}
fetchDashboardData();
}, []);
if (isLoading) {
return <h2>Loading...</h2>;
}
return (
<div>
<h2>Dashboard</h2>
<h2>Posts - {dashboardData.posts}</h2>
<h2>Likes - {dashboardData.likes}</h2>
<h2>Followers - {dashboardData.followers}</h2>
<h2>Following - {dashboardData.following}</h2>
</div>
);
}
export default Dashboard;
4.SWR for Client-side Data Fetching
- https://swr.vercel.app/zh-CN
- 数据更新时不需要刷新页面,直接展示最新数据
1)pages/dashboard-swr.js
import useSWR from "swr";
const fetcher = async () => {
const response = await fetch("http://localhost:4000/dashboard");
const data = await response.json();
return data;
};
function DashboardSWR() {
const { data, error } = useSWR("dashboard", fetcher);
if (error) return "An error has occurred.";
if (!data) return "Loading...";
return (
<div>
<h2>Dashboard</h2>
<h2>Posts - {data.posts}</h2>
<h2>Likes - {data.likes}</h2>
<h2>Followers - {data.followers}</h2>
<h2>Following - {data.following}</h2>
</div>
);
}
export default DashboardSWR;
(六)Pre-rendering + Client-side Data Fetching
1)db.json
{
"events": [
{
"id": 1,
"title": "Event 1",
"description": "Description 1",
"category": "sports",
"date": "April 25"
},
{
"id": 2,
"title": "Event 2",
"description": "Description 2",
"category": "technology",
"date": "May 25"
},
{
"id": 3,
"title": "Event 3",
"description": "Description 3",
"category": "food",
"date": "October 25"
},
{
"id": 4,
"title": "Event 4",
"description": "Description 4",
"category": "art",
"date": "December 25"
},
{
"id": 5,
"title": "Event 5",
"description": "Description 5",
"category": "music",
"date": "February 28"
}
],
"dashboard": {
"posts": 5,
"likes": 100,
"followers": 20,
"following": 50
},
"news": [
{
"id": 1,
"title": "News Article 1",
"description": "Description 1",
"category": "sports"
},
{
"id": 2,
"title": "News Article 2",
"description": "Description 2",
"category": "politics"
},
{
"id": 3,
"title": "News Article 3",
"description": "Description 3",
"category": "sports"
}
],
"products": [
{
"id": 1,
"title": "Product 1",
"price": 1000,
"description": "Description 1"
},
{
"id": 2,
"title": "Product 2",
"price": 2000,
"description": "Description 2"
},
{
"id": 3,
"title": "Product 3",
"price": 2500,
"description": "Description 3"
}
]
}
2)pages/events.js
import { useState } from "react";
import { useRouter } from "next/router";
function EventList({ eventList }) {
const [events, setEvents] = useState(eventList);
const router = useRouter();
const fetchSportsEvents = async () => {
const response = await fetch(`http://localhost:4000/events?category=sports`);
const data = await response.json();
setEvents(data);
router.push("/events?category=sports", undefined, { shallow: true });
};
return (
<>
<button onClick={fetchSportsEvents}>Sports Events</button>
<h1>List of events</h1>
{events.map((event) => {
return (
<div key={event.id}>
<h2>
{event.id} {event.title} {event.date} | {event.category}
</h2>
<p>{event.description}</p>
<hr />
</div>
);
})}
</>
);
}
export default EventList;
export async function getServerSideProps(context) {
const { query } = context;
const { category } = query;
const queryString = category ? "catrgory=sports" : "";
const response = await fetch(`http://localhost:4000/events?${queryString}`);
const data = await response.json();
return {
props: {
eventList: data,
},
};
}
(七)Summary
- 预渲染是指提前生成
HTML的过程,使应用有更好的性能和SEO NextJS支持两种形式的预渲染Static Generation静态渲染Server-side Rendering服务器端渲染
1.SG 渲染
- 在构建时生成
HTML页面的预渲染方法 - 页面一经构建,就会由
CDN缓存,并几乎立即返回给客户端- 例子:市场营销网站、博客网站
- 对于普通页面,使用
getStaticProps函数提前获取数据 - 对于动态页面,使用
getStaticProps和getStaticPaths函数提前获取数据fallback: false | true | 'blocking'
- 如果不重新构建则无法更新页面
Incremental Static Regeneration
2.SSR 渲染
- 在请求时获取数据
- 基于传入请求中的用户信息个性化数据展示
- 例子:新闻列表页面
- 使用
getServerSideProps函数帮助获取 SSR 数据 - 将预渲染和客户端数据获取相结合
Shallow routing浅路由- 不调用
getStaticProps或getServerSideProps进行路由导航
- 不调用
